|
GLsun Science & Tech Co., Ltd
|
GLSUN 50G 80ch TAWG Arrayed Waveguide Gratings
| Price: | 100.0 USD |
| Payment Terms: | T/T,L/C |
| Place of Origin: | Guangxi, China (Mainland) |
|
|
|
| Add to My Favorites | |
| HiSupplier Escrow |
Product Detail
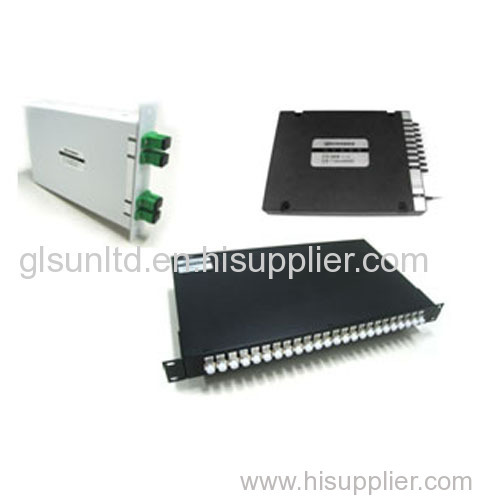
1.The specifications serve for C-band 100GHz Flat-top MUX/DEMUX in DWDM system.
2.AWG module includes an integrated internal thermal control circuit.
Arrayed waveguide gratings (AWG) are commonly used as optical (de)multiplexers in wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) systems. These devices are capable of multiplexing a large number of wavelengths into a single optical fiber, thereby increasing the transmission capacity of optical networksconsiderably.
The devices are based on a fundamental principle of optics that light waves of different wavelengths interfere linearly with each other. This means that, if each channel in an optical communication network makes use of light of a slightly different wavelength, then the light from a large number of these channels can be carried by a single optical fiber with negligible crosstalk between the channels. The AWGs are used to multiplex channels of several wavelengths onto a single optical fiber at the transmission end and are also used as demultiplexers to retrieve individual channels of different wavelengths at the receiving end of an optical communication network.
Application Note
1. The specifications serve for C-band 100GHz Flat-top MUX/DEMUX in DWDM system.
2. The AWG module includes an integrated internal thermal control circuit.
Optical Specifications
Optical signal transmission characteristics
Parameters | Notes | Specifications | Units | |
Min | Max | |||
Channels | 80 | Ch | ||
Channel Spacing | 50 | GHz | ||
Reference Pass-band | Relative to ITU Grid | ± 0.05 | nm | |
ITU Frequency | C-band | 192.1 | 196.05 | THz |
ITU Wavelength | C-band | 1529.163 | 1560.606 | nm |
Center Wavelength Accuracy | Maximum of the absolute deviation of the 3 dB center wavelength from ITU grid over all channels | ± 0.024 | nm | |
0.5 dB Bandwidth | 0.5 dB from min Insertion Loss, full width, worst case polarization | 0.1 | nm | |
1dB Bandwidth | 1dB from min Insertion Loss, full width, worst case polarization | 0.2 | nm | |
3dB Bandwidth | 3 dB from min Insertion Loss, full width, worst case polarization | 0.3 | nm | |
20 dB bandwidth | 20 dB from min Insertion Loss, full width, worst case polarization | 0.6 | nm | |
Insertion Loss | Maximum of the insertion loss across the ITU pass-band over all channels | 7.0 | dB | |
Ripple | Maximum of the loss variance across the ITU pass-band over all channels | 0.5 | dB | |
Insertion Loss Uniformity | Maximum insertion loss variance across all channels | 1.5 | dB | |
Adjacent Channel Isolation | Ratio of peak transmission to the maximum transmission over both adjacent pass-bands | 25 | dB | |
Non-Adjacent Channel Isolation | Ratio of peak transmission in channel pass- bands to maximum transmission over all non- adjacent pass-bands | 30 | dB | |
Total Crosstalk | Ratio of power in channel to power in all other pass-bands | 20 | dB | |
Polarization Dependent Loss | Maximum ratio of transmissions over all polarization states, over the ITU pass-band | 0.5 | dB | |||
Return Loss | 40 | dB | ||||
Polarization Mode Delay (PMD) | In Reference Passband over all channels | 0.5 | ps | |||
Chromatic Dispersion | In Reference Passband over all channels | -20 | 20 | ps/nm |
All parameters are the worst-case across clear ITU window, over all temperature range (-5°C to 65°C) and all states of polarization. Connector loss is included.
Environmental Conditions and Maximum Ratings
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||